Chances are, if you’ve visited a music festival, water park, hotel or convention in the last couple of years, you've probably worn an RFID wristband. But how do RFID wristbands work?
You might have even used an RFID wristband to tap and pay for drinks or post a photo to your Facebook account.
Not quite following me?
Well, here at ID&C we receive lots of questions about RFID wristband technology; how it works and more importantly, what the benefits are for event organizers.
So, we wanted to explain it plain and simple. A beginner's guide if you will. An 'RFID wristband 101', if you please...
RFID technology stands for Radio Frequency Identification, but what is that exactly?
RFID describes the method or process of transmitting the unique identity of a wristband (or any RFID-enabled object) using radio waves.
The technology enables specialist readers or 'scanners' to capture the data on an RFID tag and transmit it to a back-end computer system without the requirement for physical contact.
What happens when an RFID wristband is scanned?
The wristband contains a tiny RFID chip, which holds data such as a unique identifier, access permissions, contact details, account information, payment details, medical records or other relevant details. The antenna connected to the RFID chip transmits and receives radio frequency signals
When read (or 'tapped'), an RFID scanner will transmit an encoded radio signal which identifies a tag. In less than a millisecond, RFID tags receive the transmission and respond with a unique identification number. The RFID reader captures the transmitted data and processes it. Depending on the application, the reader may grant access, process payments, update records, or trigger specific actions based on the received information.
The most simple every-day comparison to RFID is a barcode on a can of soda.
When scanned, the barcode talks to a database of information relating to the soda. Details including product name, price, weight and use-by-date are unlocked when a barcode is read.
So, are RFID wristbands the same as barcode wristbands?
No. Not even close.
While the principle of retrieving data via scanning is the same, the similarities between RFID and bar codes end there.
I could write at length about the differences but this handy table provides a quick overview.
RFID vs Barcode Wristbands Comparison Table
| RFID Wristband | Barcode Wristband | |
| Read Rate | High throughput. Thousands of tags can be read in just a few minutes, making it ideal for event admissions. | Very low throughput. Codes can only be one at a time. |
| Line of Sight | Not required. If the tag is in reading distance, no particular orientation is required. An RFID wristband can be read from any direction, even from the back of the tag. | Required! Scanners need to see the barcode to have the ability to scan. The barcode must be oriented in a specific direction. Event organizers find this impractical. The barcode must stay perfectly clean to be read too. |
| Resource | Low. RFID can be automated via a portal, or integrated gate, allowing patrons to tap their tag on entry to an event. | High. Almost always requires human interaction to ensure accurate scanning. |
| Read/Write Capability | Read, write, and even modify in real-time. | Read only. |
| Durability | High. RFID antennas can be embedded in various, non-conductive materials for protection from water, heat and knocks. | Low. Barcodes become damaged in poor weather conditions. Bar codes need to be in perfect reading condition. |
| Security | High. RFID is difficult to copy. Tags and the database they access can be encrypted and protected by a password. This is a reason why RFID wristbands are being used in place of paper tickets at concerts and festivals. | Low. Easy to reproduce, copy and counterfeit. Barcode concert tickets can be easily faked - here's how to check if they're genuine. |
Inside an RFID Wristband
An RFID wristband contains a 'smart tag' made up of an RFID chip and antenna. The tag can be in the form of a visible card (often made from plastic for durability) or it can be hidden or 'embedded' in other wristband materials like silicone and cloth.
There are three types of tags that can be used: passive, active, and battery-assisted
- Passive – Passive RFID tags utilize energy transmitted by the reader for power and do not have a battery built-in. Passive is the most popular for large scale outdoor events and venues.
- Active – Active RFID tags have an on-board battery, which transmits information regularly without requiring a reader.
- Battery-Assisted – Battery-Assisted RFID tags contains a battery that only powers the tag when it’s in proximity of a reader.
If you want to get really technical then RFID Journal has a great FAQ on everything to do with RFID.
There are limits on the ranges RFID wristbands can meet, and depending on what type of event or festival you are planning you can choose options from low to ultra-high frequency.
How much data can an RFID wristband store?
The types of data you will find stored on RFID tags can include identification credentials, purchasing credits, coupons, access control into hotels or VIP areas, and even social media information.
So when you walk through a checkpoint, you can choose to have your activity or photos posted to social media automatically.
These types of information don’t usually require too much data to hold them.
The biggest passive RFID tags can store up to 3720 bytes, or 3.72 kilobytes of information. This is enough to store personal data, such as someone’s name, address, credit card authorization, and identifying information.
UHF (ultra high frequency) tags store up to 8 kilobytes of information.
For access control systems, RFID tags are usually 3 kilobytes or smaller.
What Data can an RFID Wristband Collect?
Using RFID technology gives organizers real-time analytics of how wearers move about and interact with your event, venue or attraction.
You can highlight busy periods, queue times, and popular attractions. Helping you constantly flex and adapt to optimize the experience for your visitors.

Can RFID wristbands be used as a Tracking Device?
Most RFID wristbands use passive tags that operate at high frequency, as such, it is impossible to track a wearers location as the tags are limited to very short distances.
However, RFID can record the last known location of a person. This can be vital and useful information for understanding traffic flow and security risks at future events.
Transform every aspect of your event, hotel or attraction
Not only does RFID technology help streamline entry, but it also connects you with your audience on a new level.
Patrons no longer have to carry wallets, tickets, and personal information just to participate. Ticket-holders can enjoy the show with a feeling of freedom.
Join the ever-growing industries that are benefiting from the use of RFID technology. Tap into how you can improve your event experience by contacting us today to find out more.
Jargon Buster
Tag / Chip: Embedded in a wristband a tag (chip) passes information, allows entry, and even payment of goods by communicating with an RFID scanner via intelligent radio signals.
Reader / Scanner: Scanners (readers) are usually positioned at entrances and exits, as well as VIP zones and other areas inside an event and communicate with a tag (chip) to carry out a task such as allowing entry, or opening a locker.
The benefits of RFID Technology for Events
Due to the security, cost-saving and revenue-increasing benefits of RFID wristband technology, many organizers are turning towards the technology to help optimize their events.
Since 2011, the live music industry, in particular, has adopted RFID technology inside concert wristbands to improve the experience for fans, increase security and open up new revenue streams.
Infographic from 2013 showing the use of RFID at music festivals.
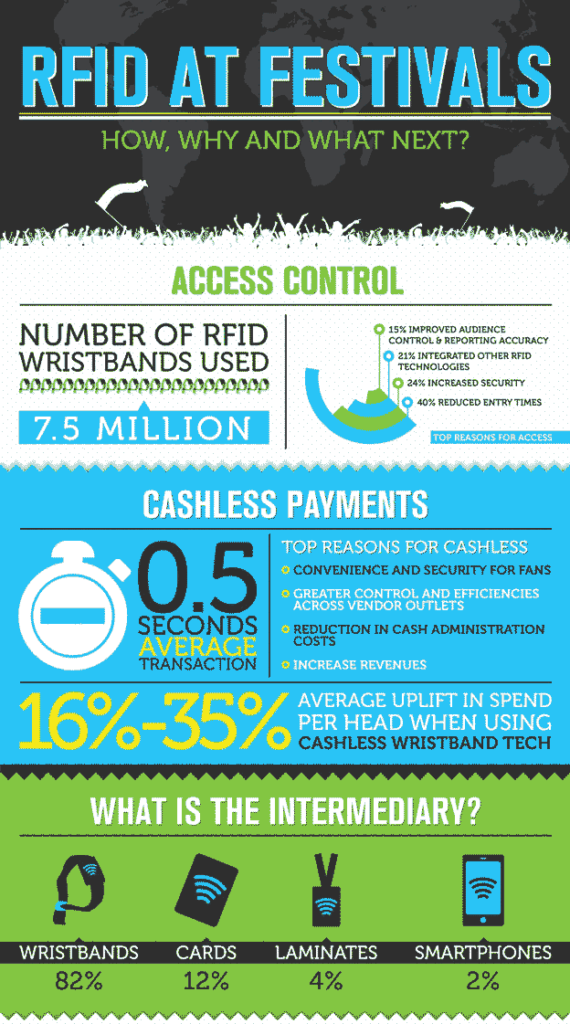
Some benefits include:
- Reduce queues
- Eliminate theft and fraud
- Build better connections with sponsors
- Go cashless
- Increase attendee engagement on-site
- Create an experience
- Collect real-time analytics
- Simplify the check-in process
- Expand the VIP experience
- Give people something to remember
Conclusion
The frictionless RFID technology is growing in popularity for events, venues and attractions due to the improved customer experience and ability to streamline operations.
FAQs
How do LED concert bracelets work?
LED concert wristbands work on the principle of infrared signals, and consist of battery-operated LEDs and signal receptors. When the light-operator at the concert venue controls the overall lighting using a computer, infrared signals are sent out that are read by the signal receptors on the wristband, lighting up the LEDs to create a unique experience for concert-goers. These LED bracelets can also be equipped with RFID tags for access control and contactless payment applications at the venue.
What’s the difference between RFID and NFC wristbands
Both RFID and NFC technology operate on the principle of transmitting and receiving data through radio frequency. However, one major difference between RFID and NFC is their range of communication between the wristband and the reader.
While data stored in RFID festival wristbands can be read by the reader from a long distance (25 to 100 meters), NFC wristbands are perfect for short-range data transfer. Another key difference between the two technologies is that RFID wristbands can only be scanned using RFID readers whereas NFC cards and wristbands can be read using a NFC-enabled smartphone. Read our article on RFID vs NFC comparison to know more.